Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /var/www/wp-content/themes/enfold/framework/php/function-set-avia-frontend.php on line 536
3: Analyzing and Recording Transactions Business LibreTexts
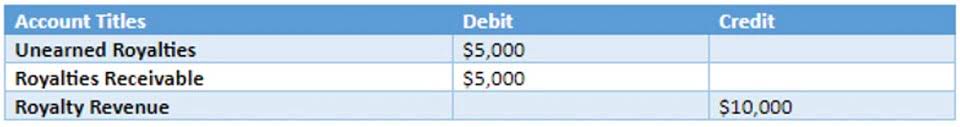
The recording of transactions in a journal must occur before they can be posted to the ledger and, ultimately, the financial statements. There are various methods of recording transactions, but the most common and simplest method is the double-entry bookkeeping system. Under this system, an accountant records each transaction in at least two different accounts, with a corresponding debit and credit entry.

You can see at the top is the name of the account “Cash,” as well as the assigned account number “101.” Remember, all asset accounts will start with the number 1. The date of each transaction related to this account is included, a possible description of the transaction, and a reference number if available. There are debit and credit columns, storing the financial figures for each transaction, and a balance column that keeps a running total of the balance in the account after every transaction.
Match records to transactions during bank reconciliations
If you use accrual accounting, you’ll want to record purchase invoices as soon as they come in and sales invoices as soon as they go out. That way amounts, dates, taxes, and customer and vendor information are automatically recorded in the software at time of issue. Looking at the charts, you see that asset and expense accounts have balance increases when they are debited and balance decreases when they are credited. In direct contrast, liability, stockholder’s equity, and revenue accounts have balance decreases when they are debited and balance increases when they are credited.
- The third step in recording business transactions is to actually document the transaction in a journal.
- Even when you’re using a computerized accounting program, items are still recorded in journals; you just don’t manually enter them.
- Accounting can be a challenge for a small business, but an organized record management system can make it easier.
- Double check that the numbers in your accounting records match the numbers on your bank statement.
One account will be debited and one account will be credited. The total of all debit entries must, therefore, equal the total of all credit entries. Expense accounts and asset accounts experience an increase with a debit entry and a decrease with a credit entry. Revenue, liability, and equity accounts experience the reverse, an increase with a credit entry and a decrease with a debit entry. Debits are entered on the left side while credits are entered on the right side. This method of double entry is important because it is what ensures that accounts remain balanced.
Resources created by teachers for teachers
This can include cash transactions, such as when a customer purchases a print cartridge from your office supply store. It also includes the payment received on an invoice for goods and services purchased on credit. The moment you record a transaction differs depending on whether you use accrual or cash accounting. With accrual accounting, you record income and expenses when invoices are sent or received, but with the cash method, you enter transactions only when the money changes hands.
Maybe it’s because a business transaction was made using cash, or a different account, or perhaps the money hasn’t actually changed hands yet. Let software lead in creating small recording transactions business accounting records, like customer invoices and payroll tax forms. A transaction is an event that occurs in a business that changes the balance of at least two accounts.
What you’ll learn to do: Account for business transactions using double-entry bookkeeping
Transaction record in accounting is defined as a business occurrence that has a monetary effect on the financial records of a firm. The first payroll transactions recorded should include gross wages as well as any payroll taxes that need to be paid. Accounting software often comes with a default chart of accounts that you can use, or you can create your own. It may be a good idea to involve an accountant or bookkeeper in setting up your chart of accounts, as your choices will affect your ability to analyze your business’s income and spending. A journal is a book where you record each business transaction shown on your supporting documents. You may have to keep separate journals for transactions that occur frequently.
You will notice that the transactions from January 3, January 9, and January 12 are listed already in this T-account. The next transaction figure of $100 is added directly below the January 12 record on the credit side. We know from the accounting equation that assets increase on the debit side and decrease on the credit side.
Business records prove business transactions and activities. Growing a successful business requires organization on all levels, including your business records. Journal entries are used to record business transactions and events. The journal entry shows that the company received computer equipment worth $1,200.
- This is posted to the Cash T-account on the debit side (left side).
- You may also have additional entries, such as bank fees and interest earned, that will need to be posted before running financial statements.
- Some of the listed transactions have been ones we have seen throughout this chapter.
- These are very important points to know when recording transactions.
- Growing a successful business requires organization on all levels, including your business records.
- A debit to an asset account increases its balance, so the balance in the accounts receivable account is increased by $985.
- Understanding who buys gift cards, why, and when can be important in business planning.

